Innovative building materials by data-driven virtual materials design
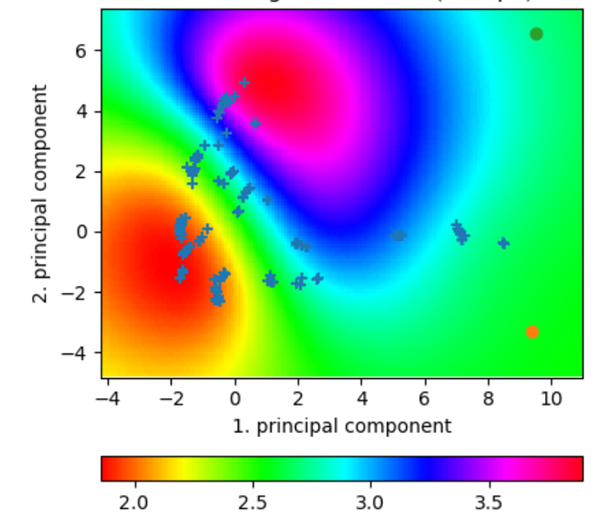
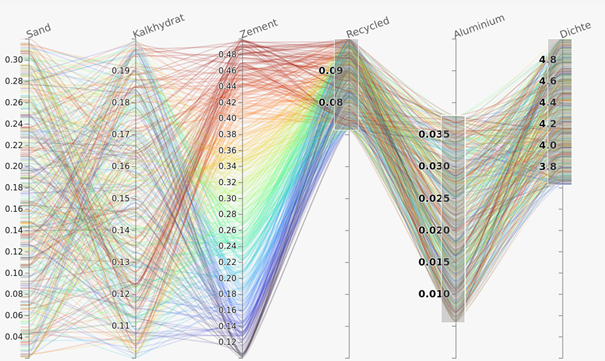
For demonstration purposes, the development and validation of a data-driven model for predicting the properties of mineral building materials, with a focus on aerated concrete, were first pursued. To this end, in a first step experimental data were collected and processed. With the help of this data collection, a model was then developed for predicting the properties of aerated concrete based on mechanical material parameters and physical data. To improve the prediction quality, this model was extended for the first time to include chemical material parameters. Furthermore, this model served as the basis for the development and implementation of a demonstrator for the inverse design of aerated concrete. Here, properties of the desired aerated concrete can be specified and the demonstrator then determines suitable formulations.
High potential to accelerate the development and optimization process of sustainable building materials
Overall, the project has shown that data-driven virtual material design has a very high potential to significantly accelerate the development and optimization process of sustainable building materials. For the first time, it was possible to develop a model for the inverse design of aerated concrete. Currently, the proposed formulations are also validated experimentally and the concept is to be implemented for other mineral building materials.
 Research Center Machine Learning
Research Center Machine Learning